Can At&t Prepaid Phones Be Used With A Regular Plan
CAN (Controller Area Network) protocol
Tin stands for Controller Area Network protocol. Information technology is a protocol that was adult by Robert Bosch in around 1986. The Tin protocol is a standard designed to allow the microcontroller and other devices to communicate with each other without whatsoever host calculator. The characteristic that makes the CAN protocol unique among other communication protocols is the circulate blazon of autobus. Hither, broadcast means that the information is transmitted to all the nodes. The node can be a sensor, microcontroller, or a gateway that allows the computer to communicate over the network through the USB cable or ethernet port. The CAN is a message-based protocol, which ways that bulletin carries the message identifier, and based on the identifier, priority is decided. There is no demand for node identification in the Can network, then it becomes very easy to insert or delete it from the network. It is a serial half-duplex and asynchronous type of communication protocol. The CAN is a 2-wired communication protocol as the CAN network is connected through the two-wired passenger vehicle. The wires are twisted pair having 120Ω characteristics impedance connected at each end. Initially, it was mainly designed for advice within the vehicles, simply it is now used in many other contexts. Like UDS, and KWP 2000, Tin can too be used for the on-board diagnostics.
Why CAN?
The demand for a centralized standard communication protocol came because of the increment in the number of electronic devices. For case, there can be more than 7 TCU for various subsystems such equally dashboard, transmission control, engine control unit of measurement, and many more in a mod vehicle. If all the nodes are connected one-to-ane, then the speed of the communication would be very high, but the complexity and cost of the wires would be very high. In the above case, a unmarried dashboard requires 8 connectors, and then to overcome this event, Tin was introduced equally a centralized solution that requires two wires, i.e., Can loftier and CAN low. The solution of using CAN protocol is quite efficient due to its message prioritization, and flexible as a node tin be inserted or removed without affecting the network.
Applications of CAN protocol
Initially, Tin can protocol was designed to target the communication issue that occurs within the vehicles. Simply later on, due to the features it offers, information technology is used in various other fields. The following are the applications of CAN protocol:
- Automotive (rider vehicles, trucks, buses)
- Electronic equipment for aviation and navigation
- Industrial automation and mechanical control
- Elevator and escalators
- Building automation
- Medical instruments and equipment
- Marine, medical, industrial, medical
CAN layered architecture
As we know that the OSI model partitions the advice system into seven different layers. Just the CAN layered architecture consists of ii layers, i.due east., data-link layer and physical layer.
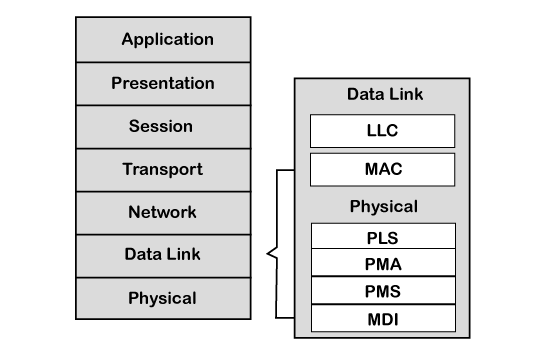
Let'southward sympathise both the layers.
- Information-link layer: This layer is responsible for node to node data transfer. It allows you to establish and cease the connectedness. It is also responsible for detecting and correcting the errors that may occur at the physical layer. Information-link layer is subdivided into ii sub-layers:
- MAC: MAC stands for Media Access Control. It defines how devices in a network proceeds access to the medium. It provides Encapsulation and Decapsulation of data, Error detection, and signaling.
- LLC: LLC stands for Logical link control. Information technology is responsible for frame acceptance filtering, overload notification, and recovery management.
- Physical layer: The concrete layer is responsible for the transmission of raw data. It defines the specifications for the parameters such every bit voltage level, timing, data rates, and connector.
CAN specifications define CAN protocol and Tin physical layer, which are divers in the CAN standard ISO 11898. ISO 11898 has three parts:
- ISO 11898-1: This function contains the specification of the Data-link layer and physical indicate link.
- ISO 11898-ii: This part comes under CAN physical layer for loftier speed Tin. The loftier- speed CAN allows information rate upto one Mbps used in the power railroad train and the charges area of the vehicle.
- ISO 11898-3: This part also comes under CAN physical layer for low-speed Can. It allows data rate upto 125 kbps, and the low speed Can is used where the speed of communication is non a critical factor.
CiA DS-102: The full form of CiA is CAN in Automation, which defines the specifications for the CAN connector.
As far as the implementation is concerned, the CAN controller and CAN transceiver are implemented in the software with the aid of the application, operating organisation, and network management functions.
CAN Framing
Let's understand the structure of the CAN frame.
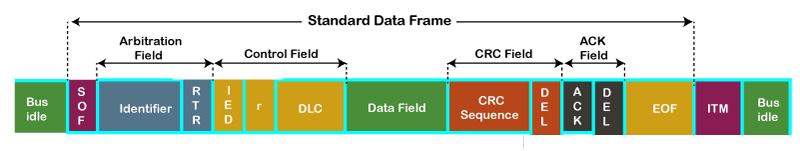
- SOF: SOF stands for the start of frame, which indicates that the new frame is entered in a network. It is of 1 bit.
- Identifier: A standard data format defined under the CAN 2.0 A specification uses an eleven-chip message identifier for arbitration. Basically, this message identifier sets the priority of the data frame.
- RTR: RTR stands for Remote Transmission Request, which defines the frame type, whether it is a data frame or a remote frame. Information technology is of 1-chip.
- Control field: It has user-defined functions.
- IDE: An IDE bit in a command field stands for identifier extension. A dominant IDE bit defines the eleven-bit standard identifier, whereas recessive IDE bit defines the 29-chip extended identifier.
- DLC: DLC stands for Information Length Lawmaking, which defines the data length in a information field. Information technology is of iv bits.
- Information field: The data field tin contain upto viii bytes.
- CRC field: The data frame also contains a cyclic redundancy check field of 15 flake, which is used to detect the corruption if it occurs during the transmission time. The sender will compute the CRC before sending the data frame, and the receiver besides computes the CRC and then compares the computed CRC with the CRC received from the sender. If the CRC does not lucifer, then the receiver will generate the fault.
- ACK field: This is the receiver's acknowledgment. In other protocols, a separate bundle for an acquittance is sent afterward receiving all the packets, but in case of CAN protocol, no separate packet is sent for an acquittance.
- EOF: EOF stands for end of frame. It contains 7 consecutive recessive bits known Finish of frame.
Now we will run across how information is transmitted through the Tin can network.
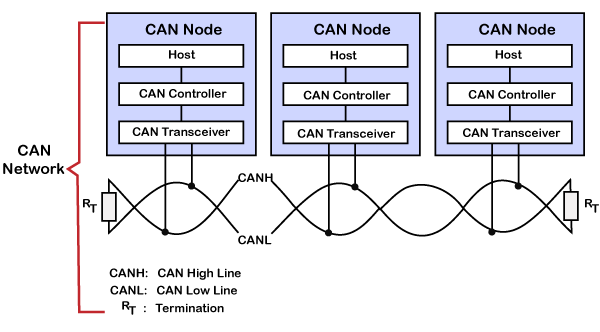
A Tin can network consists of multiple of CAN nodes. In the above instance, we have considered three Can nodes, and named them as node A, node B, and node C. CAN node consists of iii elements which are given below:
- Host
A host is a microcontroller or microprocessor which is running some application to do a specific chore. A host decides what the received message means and what bulletin it should transport next. - Tin Controller
Tin controller deals with the communication functions described by the Tin protocol. It too triggers the transmission, or the reception of the Tin can messages. - CAN Transceiver
Tin transceiver is responsible for the transmission or the reception of the information on the CAN bus. It converts the data signal into the stream of data collected from the CAN bus that the CAN controller can understand.
In the higher up diagram, unshielded twisted pair cable is used to transmit or receive the data. It is also known equally Can bus, and Can bus consists of 2 lines, i.eastward., CAN low line and Tin can high line, which are too known equally CANH and CANL, respectively. The transmission occurs due to the differential voltage applied to these lines. The Tin can uses twisted pair cablevision and differential voltage because of its environs. For instance, in a car, motor, ignition system, and many other devices can crusade data loss and data corruption due to racket. The twisting of the two lines also reduces the magnetic field. The bus is terminated with 120Ω resistance at each cease.
CAN Characteristics
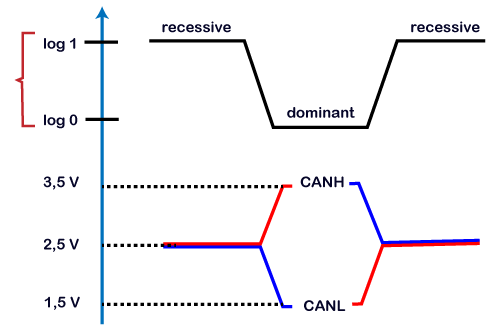
With the aid of differential voltage, we will determine how 0 and ane are transmitted through the CAN charabanc. The above effigy is the voltage graph that shows the voltage level of CAN low and CAN high. In CAN terminology, logic 1 is said to exist recessive while logic 0 is ascendant. When CAN loftier line and Tin low line are applied with 2.5 volts, then the actual differential voltage would be nothing volt. A nil volt on CAN bus is read by the Tin transceiver as a recessive or logic one. A zero volt on CAN bus is an ideal state of the bus. When Tin high line is pulled upward to 3.five volt and the Can low line is pulled down to i.five volt, and so the bus's actual differential voltage would exist 2 volts. Information technology is treated every bit a dominant bit or logic 0 by the Tin transceiver. If the bus country is reached to dominant or logic 0 then it would get impossible to motion to the recessive country by any other node.
Fundamental points learnt from the CAN characteristics
- Logic 1 is a recessive state. To transmit 1 on CAN bus, both CAN high and Tin low should be applied with two.5V.
- Logic 0 is a dominant country. To transmit 0 on Tin jitney, Tin high should be applied at 3.5V and CAN depression should exist applied at 1.5V.
- The platonic state of the bus is recessive.
- If the node reaches the ascendant state, information technology cannot movement back to the recessive land past any other node.
CAN bus logic
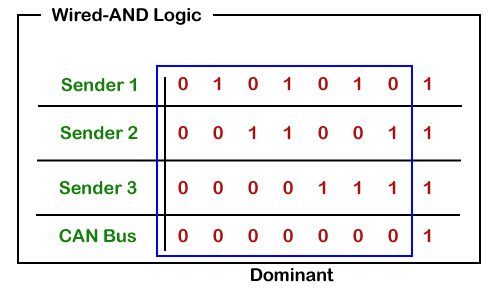
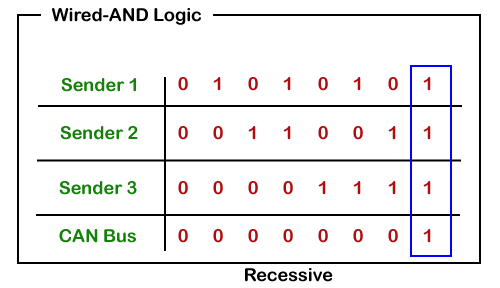
From the above scenario, nosotros get to know that the dominant country overwrites the recessive state. When the node sends the dominant and the recessive chip simultaneously, so the omnibus remains dominant. The recessive level occurs only when all the nodes ship the recessive bit. Such logic is known as AND logic, and physically it is implemented as an open collector circuit.
CAN Communication Principle
Every bit we know that the bulletin is sent based on the priority fix in the arbitration field. For the standard frame, the message identifier is 11 bit, while for the extended frame, the message identifier is 29 flake. It allows the arrangement designer to design the message identifier at the design itself. The smaller the message identifier, the higher, would exist the bulletin priority.
Let's understand how arbitration works through a flow nautical chart.
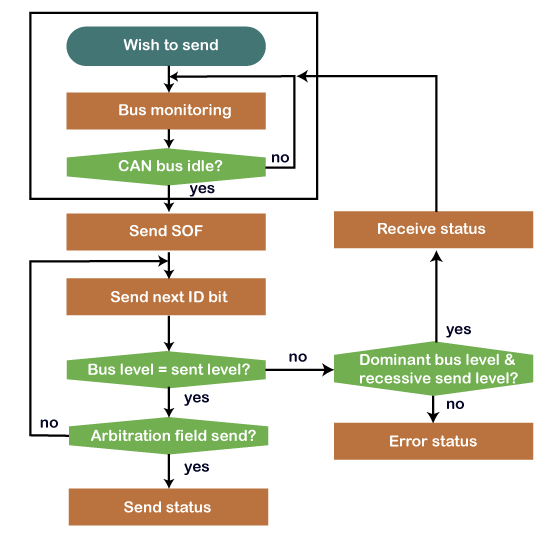
The sender wants to send the message and waiting for the Tin bus to get idle. If the CAN autobus is idle, and then the sender sends the SOF or the ascendant flake for the autobus access. And then, it sends the message identifier scrap in the most pregnant chip. If the node detects the dominant flake on the coach while information technology has transmitted the recessive bit, information technology means that the node has lost the arbitration and stops transmitting further $.25. The sender volition expect and resend the message once the jitney is free.
CAN Mediation Instance
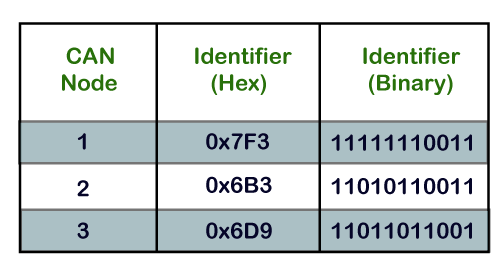
If nosotros consider iii nodes, i.e., Node 1, Node ii, and Node iii, the message identifiers of these nodes are 0x7F3, 0x6B3, and 0x6D9, respectively.
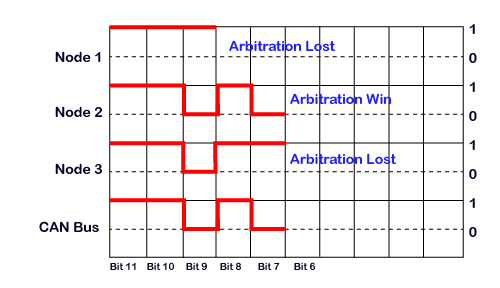
The transmission of all the three nodes with the about pregnant fleck is shown in the above diagram.
11th bit: As all the three bits of nodes are recessive, then motorcoach fleck will also remain recessive.
10thursday bit: All the nodes have 10th fleck equally recessive, so the motorcoach will also remain recessive.
9th bit: Node 1 has recessive scrap while other nodes take a ascendant bit, so the jitney will likewise remain dominant. In this case, node one has lost the mediation, and so it stops sending bits.
viiith bit: Both node 2 and node three are sending recessive bit, so that the bus country will remain recessive.
seventh bit: The node two is sending dominant bit while node 3 has sent recessive fleck, so that the bus state will remain dominant. In this example, the node 3 has lost the arbitration, and then it stops sending the message while the node 2 has won the arbitration means that it volition continue to concord the coach until the message is received.
Can At&t Prepaid Phones Be Used With A Regular Plan,
Source: https://www.javatpoint.com/can-protocol
Posted by: handyowly1985.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Can At&t Prepaid Phones Be Used With A Regular Plan"
Post a Comment